| lib | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| cl_01.png | ||
| LICENSE-MIT | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
readlineSync
Synchronous Readline for interactively running.
The interface is used with process.stdin and process.stdout in order to accept user input.
Example
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync');
var answer = readlineSync.question('What is your favorite food? :');
console.log('Oh, so your favorite food is ' + answer);
Installation
npm install readline-sync
Usage
setPrompt
currentValue = readlineSync.setPrompt([prompt])
Sets the prompt, for example when you run node on the command line, you see > , which is node's prompt.
prompt may be string, or may not be (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). This is converted to string (i.e. toString method is called) before it is displayed every time.
For example: [foo-directory]# like a bash
// Object that has toString method.
readlineSync.setPrompt({toString: function() {
return '[' + require('path').basename(process.cwd()) + ']# ';
}})
prompt
line = readlineSync.prompt([options])
Readies readline for input from the user, putting the current setPrompt options on a new line, giving the user a new spot to write.
If {noEchoBack: true} is specified to options, echo back is avoided. It is used to hide the secret text (e.g. password) which is typed by user on screen.
question
line = readlineSync.question([query[, options]])
Displays the query to the user, and then returns the user's response after it has been typed.
query may be string, or may not be (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). This is converted to string (i.e. toString method is called) before it is displayed.
If {noEchoBack: true} is specified to options, echo back is avoided. It is used to hide the secret text (e.g. password) which is typed by user on screen.
setEncoding
currentValue = readlineSync.setEncoding([encoding])
Set the encoding method of input (user's response) and output (prompt and question). Defaults to 'utf8'.
setPrint
readlineSync.setPrint([funcPrint])
The specified Function is called when any output (prompt and question). Defaults to undefined.
The Function is given two arguments the output text and encoding.
For example, this is used to pass plain texts to Logger, when texts are colored.
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync'),
user, pw, cmd;
require('colors');
readlineSync.setPrint(function(display, encoding) {
logger.log(display.stripColors); // remove control characters
});
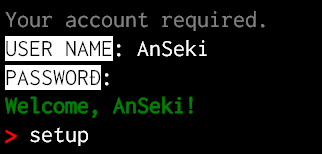
console.log('Your account required.'.grey);
user = readlineSync.question('USER NAME'.white.inverse + ': ');
pw = readlineSync.question('PASSWORD'.white.inverse + ': ', {noEchoBack: true});
// Authorization ...
console.log(('Welcome, ' + user + '!').green.bold);
readlineSync.setPrompt('> '.bold.red);
cmd = readlineSync.prompt();
With Task Runner
The easy way to control the flow of task runner by the user's response:
- Grunt plugin: grunt-confirm
- gulp plugin: gulp-confirm
If you want to control the flow of task runner (e.g. Grunt), call readlineSync in a task callback that is called by task runner. Then the flow of tasks is paused and it is controlled by user.
Example: by using grunt-task-helper
$ grunt
Running "fileCopy" task
Files already exist:
file-a.png
file-b.js
Overwrite? (y/n) :y
file-a.png copied.
file-b.js copied.
Done.
Gruntfile.js
grunt.initConfig({
taskHelper: {
fileCopy: {
options: {
handlerByTask: function() {
// Abort the task if user don't want.
return readlineSync.question('Overwrite? (y/n) :')
.toLowerCase() === 'y';
// Or process.exit()
},
filesArray: []
},
...
}
},
copy: {
fileCopy: {
files: '<%= taskHelper.fileCopy.options.filesArray %>'
}
}
});
Note
Platforms
The your Node and OS may not support interactively reading from stdin. The stdin interfaces are different by platforms.
If in those platforms, an error is thrown.
try {
answer = readlineSync.question('What is your favorite food? :');
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
}
Reading by shell
readlineSync tries reading from stdin by shell if it is needed. And, it use "piping via files" for synchronous running.
As everyone knows, "piping via files" is no good. It blocks event loop and a process. It may make your script be slow.
Why did I choose it? :
- The best solution is child_process.execSync in core modules of Node. But it is not supported by current version.
- The good modules (native addon) for synchronous execution exist. But node-gyp can't compile those in some platforms or Node versions.
- I think that the security is important more than the speed. Some modules have problem about security. (Those don't protect data.) I think that the speed is not needed usually, because readlineSync is used while user types keys.
Someday, I may rewrite readlineSync to use child_process.execSync, or safety module.
Release History
- 2014-09-12 v0.4.8 fixed #9: Error of
sttyin read.sh. - 2014-07-13 v0.4.3 fixed #6: Crypto input data.
- 2014-07-12 v0.4.2
setPrompt()andsetEncoding()return current value. - 2014-07-12 v0.4.1
setPrompt()andquestion()accept the value which is not string too (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). - 2014-07-12 v0.4.0 Add
options.noEchoBack. - 2014-07-12 v0.3.0 Add
setPrint(). - 2014-06-27 v0.2.3 Add alternative reading via shell on the environment which don't support interactively reading.
- 2013-12-18 v0.2.2 Error handle for the environment which don't support interactively reading from stdin.
- 2013-08-30 v0.2.0 Rewrite exporting methods.
- 2013-08-29 v0.1.0 Initial release.