| lib | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| cl_01.png | ||
| cl_02.png | ||
| LICENSE-MIT | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
readlineSync
Synchronous Readline for interactively running to have a conversation with the user via a console(TTY).
readlineSync tries to let your script have a conversation with the user via a console, even when the input/output is redirected like your-script <foo.dat >bar.log.
Example
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync');
var userName = readlineSync.question('May I have your name? :'); // Wait for user's response.
var favFood = readlineSync.question('Hi ' + userName + '! What is your favorite food? :');
console.log('Oh, ' + userName + ' likes ' + favFood + '!');
May I have your name? :CookieMonster
Hi CookieMonster! What is your favorite food? :tofu
Oh, CookieMonster likes tofu!
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync');
// The user does not have to press an Enter key.
if (readlineSync.keyInYN('Do you want this module?')) {
// 'Y' key was pressed.
installModule();
} else {
searchAnother();
}
Installation
npm install readline-sync
Input Methods
question
answer = readlineSync.question([query[, options]])
Display the query to the user, and then return the user's response after it has been typed and Enter key was pressed.
You can specify options (see Options). If the user inputs the secret text (e.g. password), you should consider noEchoBack option.
The query may be string, or may not be (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). This is converted to string (i.e. toString method is called) before it is displayed.
prompt
input = readlineSync.prompt([options])
Display the current prompt (see setPrompt method) to the user, and then return the user's response after it has been typed and Enter key was pressed.
You can specify options (see Options). If the user inputs the secret text (e.g. password), you should consider noEchoBack option.
keyIn
pressedKey = readlineSync.keyIn([query[, options]])
Display the query to the user, and then return the character as the pressed key by the user, without pressing the Enter key.
You can specify options (see Options).
Note that the user has no chance to change the input.
The query may be string, or may not be (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). This is converted to string (i.e. toString method is called) before it is displayed.
Setting Methods
setPrompt
currentPrompt = readlineSync.setPrompt([newPrompt])
Set the prompt, for example when you run node on the command line, you see > , which is Node's prompt. The default is '> '. (see prompt method)
The newPrompt may be string, or may not be (e.g. number, Date, Object, etc.). This is converted to string (i.e. toString method is called) before it is displayed every time.
For example, [foo-directory]# like a bash shell that show the current directory.
// Simple Object that has toString method.
readlineSync.setPrompt({
toString: function() {
return '[' + require('path').basename(process.cwd()) + ']# '; // Get and show current directory.
}
});
setPrint
readlineSync.setPrint([callback])
The specified callback Function is called when any outputs are done by Input Methods. The callback is given two arguments, display as the output text, and encoding (see setEncoding method).
For example:
- This is used to pass the plain texts to the Logger, when the texts are colored.
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync'),
chalk = require('chalk'),
user, pw, command;
readlineSync.setPrint(function(display, encoding) {
logger.log(chalk.stripColor(display)); // Remove control characters.
});
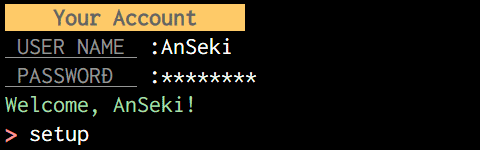
console.log(chalk.black.bold.bgYellow(' Your Account '));
user = readlineSync.question(chalk.gray.underline(' USER NAME ') + ' :');
pw = readlineSync.question(chalk.gray.underline(' PASSWORD ') + ' :', {noEchoBack: true});
// Authorization ...
console.log(chalk.green('Welcome, ' + user + '!'));
readlineSync.setPrompt(chalk.red.bold('> '));
command = readlineSync.prompt();
- Like
your-script >foo.log, when the output is redirected to record those into a file, this is used to output the conversation to the file. That is, the conversation isn't outputted tofoo.logwithout this code.
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync');
readlineSync.setPrint(function(display, encoding) {
console.log(display); // Output to STDOUT (foo.log)
});
setMask
currentMask = readlineSync.setMask([newMask])
Set the mask character that is shown instead of the secret text (e.g. password) when noEchoBack option is true (see noEchoBack option). The default is '*'. If you want to show nothing, specify ''. (But it might be not user friendly in some cases.)
Note: In some cases (e.g. when the input is redirected on Windows XP), '*' or '' might be used always.
For example:
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync'),
chalk = require('chalk'),
secret;
readlineSync.setMask(chalk.magenta('\u2665'));
secret = readlineSync.question('Please whisper sweet words :', {noEchoBack: true});
setBufferSize
currentBufferSize = readlineSync.setBufferSize([newBufferSize])
When readlineSync reads from a console directly (without external program), a size newBufferSize buffer is used. Even if the user's response exceeds it, it's usually no problem, because the buffer is used repeatedly. But, some platforms's (e.g. Windows) console might not accept user's response that exceeds it. And set an enough size. The default is 1024.
setEncoding
currentEncoding = readlineSync.setEncoding([newEncoding])
Set the encoding method of input (user's response) and output by Input Methods. The default is 'utf8'.
Options
An options Object can be specified to Input Methods. This Object can have following properties.
noEchoBack
Type: Boolean
Default: false
If true is specified, the secret text (e.g. password) which is typed by user on screen is hidden by the mask characters (see setMask method).
For example:
password = readlineSync.question('PASSWORD :', {noEchoBack: true});
console.log('Login ...');
The typed text is not shown on screen.
PASSWORD :********
Login ...
limit
Limit the user's input.
For keyIn method
Type: string or Array
Default: ''
The method doesn't return until the specified key is pressed.
Specify the characters as the key. All strings or Array of those are decomposed into single characters. For example, 'abcde' is the same as ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] or ['a', 'bc', ['d', 'e']].
For example:
if (readlineSync.keyIn('Are you sure? :', {limit: 'yn'}) === 'y') { // Accept 'y' or 'n'
execSomething();
} else {
process.exit();
}
caseSensitive
Type: Boolean
Default: false
By default, the matching is case-insensitive when limit option (see limit option) is specified (i.e. a equals A). If true is specified, the matching is case-sensitive (i.e. a is different from A).
noTrim
Type: Boolean
Default: false
By default, the leading and trailing white spaces are removed from the typed text that is returned by Input Methods except keyIn method. If true is specified, those are not removed.
With Task Runner
The easy way to control the flow of task runner by the user's response:
- Grunt plugin: grunt-confirm
- gulp plugin: gulp-confirm
If you want to control the flow of task runner (e.g. Grunt), call readlineSync in a task callback that is called by task runner. Then the flow of tasks is paused and it is controlled by user.
Example: by using grunt-task-helper
$ grunt
Running "fileCopy" task
Files already exist:
file-a.png
file-b.js
Overwrite? (y/n) :y
file-a.png copied.
file-b.js copied.
Done.
Gruntfile.js
grunt.initConfig({
taskHelper: {
fileCopy: {
options: {
handlerByTask: function() {
// Abort the task if user don't want.
return readlineSync.question('Overwrite? (y/n) :')
.toLowerCase() === 'y';
// Or process.exit()
},
filesArray: []
},
...
}
},
copy: {
fileCopy: {
files: '<%= taskHelper.fileCopy.options.filesArray %>'
}
}
});
Note
Platforms
The TTY interfaces are different by platforms. If the platform doesn't support interactively reading from TTY, an error is thrown.
try {
answer = readlineSync.question('What is your favorite food? :');
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
}
Reading by External Program
readlineSync tries to read from a console by using the external program if it is needed (e.g. when the input is redirected on Windows XP). And if the running Node doesn't support the Synchronous Process Execution (i.e. Node v0.10-), readlineSync uses "piping via files" for synchronous running.
As everyone knows, "piping via files" is no good. It blocks the event loop and a process. It may make your script be slow.
Why did I choose it? :
- The good modules (native addon) for synchronous execution exist. But node-gyp can't compile those in some platforms or Node versions.
- I think that the security is important more than the speed. Some modules have problem about security. (Those don't protect data.) I think that the speed is not needed usually, because readlineSync is used while user types keys.